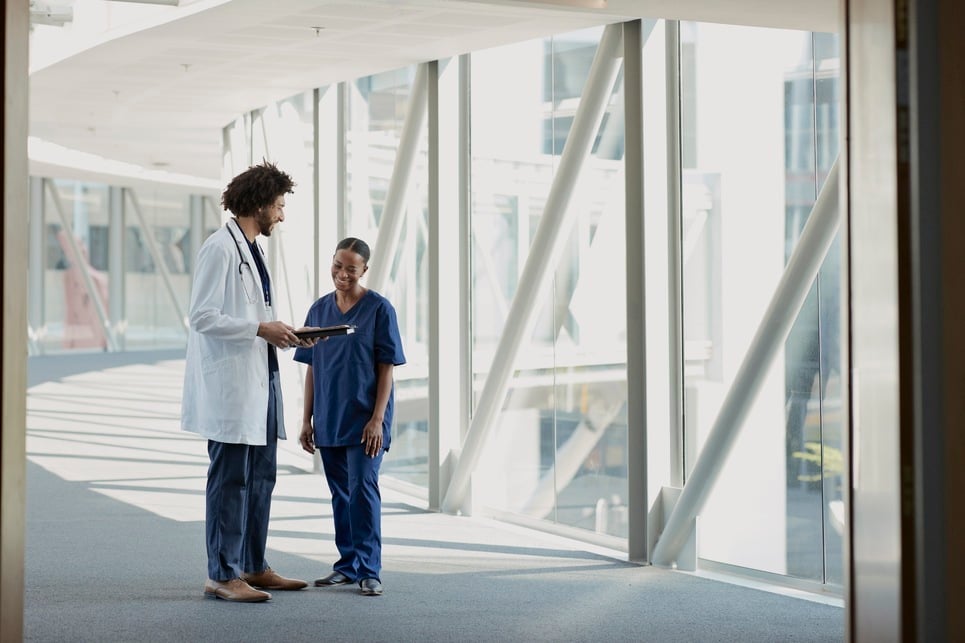

By CereCore | Apr 25, 2025
5 minute read Blog| Infographic / Checklist
Our latest survey of healthcare executives, all members of CHIME (College of Healthcare Information Management Executives), revealed a range of innovative strategies and priorities that organizations are adopting to navigate current challenges and drive efficiency. Notably, the size of an organization plays a crucial role in how IT challenges are managed. To illustrate those differences, we categorized our survey results into two groups: smaller hospitals (≤ 250 beds) and larger hospitals (250+ beds). This division underscores the varying IT decision-making processes based on hospital size.
IT Decision-Making in Healthcare
In smaller organizations, the CIO is the primary IT decision maker – responsible for determining IT spending and setting IT priorities (76%). Similarly, in larger hospitals, 67% of respondents identified the CIO as the top decision-maker. However, the “Other” category, which includes responses containing “Mix”, “Combination”, and “A team of leaders”, comes in a close second for larger hospitals. Highlighting the nuanced differences in decision-making processes between smaller and larger organizations.
IT Budget Disparities
When it comes to IT budgets, there is a significant disparity between small and large hospitals. CIOs from smaller hospitals (35%) indicated ≤3% of their Net Patient Revenue (NPR) is budgeted for IT. We also found that 12% of respondents in the “Other” category, in their free-text response indicated 10% of their NPR is allocated to IT, highlighting a notable difference within smaller hospitals. In contrast, participants from larger hospitals reported that 4% of the NPR is budgeted for IT (43%). Indicating a more consistent approach to IT budgeting with smaller hospitals.
For larger hospitals, allocation to operational versus capital expenses remain consistent, with 75% of an organization's IT budget allocated toward operational expenses and 25% to capitol expenses in both 2023 and 2024. However, smaller hospitals reported a shift in their budget allocation. In 2023, respondents indicated an even 50/50 split (53%) between operational and capital expenses. By 2024, this shifted to 75% operational and 25% capital (59%).
Both small and large hospitals find common ground when it comes to IT initiatives projected to receive the most budget in 2025. Cybersecurity is identified as the top priority, followed by EHR/EPR implementation as the second priority in both types of organizations.
This analysis underscores the various approaches to IT budgeting and priorities between smaller and larger healthcare organizations, reflecting their unique challenges and shared strategies.
Staffing Challenges in Healthcare IT
Regardless of size, hospitals face staffing challenges to varying degrees. Interestingly, both small and large organizations report a low turnover rate for IT positions at ≤5%. These findings suggest that once IT professionals are hired, they tend to stay, which may be due to factors that go beyond hospital size, such as job satisfaction and effective retention strategies. While turnover rates are low, this consistency in responses extends to the skills that are hardest to recruit and retain, with both types of organizations identifying cybersecurity as the top skill in demand. With the growing importance of cybersecurity in healthcare and the demand being high for cybersecurity professionals, this common challenge is expected.
When addressing staffing challenges, smaller hospitals are more likely to reassign work or reorganize their current IT staff (59%). In contrast, larger hospitals tend to address these challenges more quickly by hiring contractors for a specific, short-term project (71%). Larger hospitals typically have more financial resources and can afford to hire contractors, allowing them to avoid long-term commitments.
Not every healthcare organization has the budget for a dedicated information security official, so virtual Chief Information Security Officers (vCISOs) have entered the scene offering new expertise and capacity for organizations who once bolted cybersecurity onto an existing officer role. Leadership teams work with a vCISO to define the scope of their work and the anticipated time to accomplish the priorities. The vCISO's knowledge of regulatory requirements and insights from a current state assessment inform the specifics of an effective security program. Learn more about the benefits of a vCISO and the results in action.
While both small and large hospitals face similar staffing challenges, their approaches to managing these issues differ significantly. Smaller hospitals are maximizing their existing resources, while larger hospitals are leveraging their financial strength. Both strategies reflect their unique constraints and advantages with each type of organization size.
Strategic Priorities for Cost Savings and Technical Debt
Technical debt is a prevalent issue in healthcare IT, affecting both small and large hospitals. For organizations with ≤250 beds, 41% of respondents report being more concerned about technical debt than in previous years. This heightened concern may stem from limited resources and maintenance and upgrading IT systems, accumulating tech debt over time.
In contrast, larger hospitals (250+ beds) have also experienced the effects of technical debt. However, the majority of respondents indicate that their level of concern remains consistent with previous years. This could suggest that larger hospitals have more established processes and resources to manage technical debt, allowing them to maintain a steady state of concern without significant increases.
Overall, technical debt remains a prevalent issue for healthcare IT across all hospital sizes, showing the importance of ongoing strategic management to ensure the efficiency of IT systems.
Measures are being taken to prevent technical debt from both sizes:
≤ 250 beds |
250+ beds |
|
|
We asked participants which areas they are most likely to pursue in order to drive cost savings and efficiency inside their organization, and the responses are telling. The emergent topic of AI is resonating with larger organizations, as 24% of CIOs rate it their top priority. This indicates that larger hospitals are both financially and technologically equipped to leverage advanced technologies like AI to enhance their operations.
In contrast, only 8% of smaller hospitals are prioritizing AI. Instead, 25% of these smaller hospitals are focusing on application rationalization and optimization. This approach suggests smaller hospitals are looking to streamline existing systems to achieve cost savings, rather than investing heavily in new technologies that will not provide an immediate outcome.
Managed Services and Advisory Priorities
Smaller hospitals are more inclined to consider managed services (71%) to offload the burden of high performing IT operations such as hosting and network management. This reliance on managed services allows smaller hospitals to extend their bandwidth and expertise to ensure quality IT operations. This might be a challenge to maintain in-house due to limited resources.
Larger hospitals, on the other hand, focus on help/service desk solutions (43%) to manage the higher volume of requests and to maintain operational efficiency. This focus reflects the larger scale of operations and the need for efficient handling of IT support requests to ensure smooth functioning. While only one third of smaller hospital systems are considering help/service desk solutions as part of making the most of the operating budget specifics mentioned above, their consideration showcases their proactive approach to maximizing spend. This demonstrates their dedication, despite budget constraints, to enhancing service quality and operations at whatever scale possible.
The advisory services most valuable to lead organizations forward show significant disparities based on hospital size. Smaller organizations find technology adoption/digital transformation consulting (example: for revenue cycle) (38%) most valuable. This indicates a focus on modernizing and optimizing their existing processes to improve efficiency. Only 6% of larger hospitals selected this option. Larger organizations are finding value in cybersecurity advisory (risk assessment, HIPAA compliance, NIST framework, technical security assessment, or architecture review) (47%). This may suggest that larger hospitals already have more advanced systems in place and are looking to receive specialized guidance to navigate regulatory requirements in their more complex environment.
Navigating the IT Landscape in Healthcare
This survey highlights the distinct strategies and priorities of small (250 beds) and large (250+ beds) healthcare organizations in navigating today’s IT landscape. Both groups have adopted innovative strategies to manage their resources effectively and prioritize cybersecurity and operational efficiency, but in their own unique way that tailors to their constraints and capabilities. Smaller organizations report focusing on maximizing resources suggesting contracted resources and revenue cycle assessments to find more funding are opportunities for systems experiencing tight budgets. Findings for larger hospital systems suggest focus on core competencies and partnership strategies for technology adoption, resilience confidence, and managed services are growing opportunities. The adaptability and strategic planning present in both sizes show the resiliency and continuous pursuit of efficiency in healthcare IT.
For more information:CereCore® provides IT services that make it easier for you to
CereCore® provides IT services that make it easier for you to
Let us know how we can support your initiatives and take some of the heavy lifting from healthcare IT.
© All Rights Reserved CereCore Terms of Service California Notice at Collection Privacy Policy Responsible Disclosure