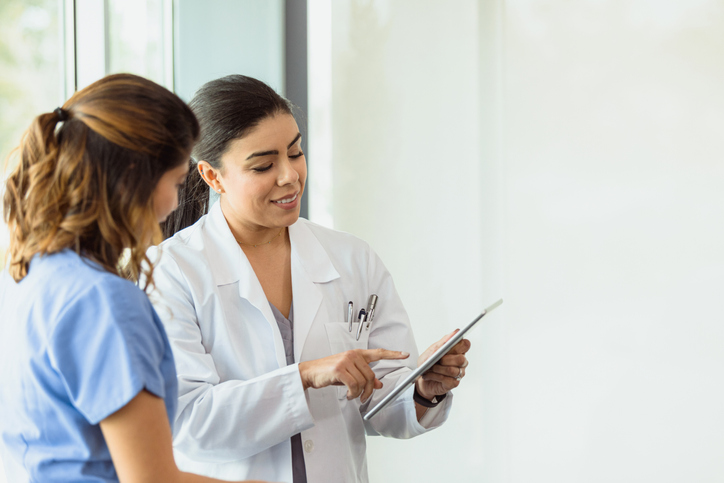

Moving patients through their hospital stay safely and efficiently is paramount to their care, satisfaction, and cost containment. Many factors contribute to a hospital’s ability to manage their average length of stay (LOS), however, you can leverage Epic to identify, improve, and/or alleviate some of those factors.
We understand the importance of healing your patients and discharging them to an appropriate level of care as quickly and safely as possible. Our experienced Epic experts can conduct the assessment noted above efficiently and effectively, providing you with recommendations that will help you achieve that goal.
CereCore® provides IT services that make it easier for you to
CereCore® provides IT services that make it easier for you to
Let us know how we can support your initiatives and take some of the heavy lifting from healthcare IT.
© All Rights Reserved CereCore Terms of Service California Notice at Collection Privacy Policy Responsible Disclosure